

Recombinant proteins are fundamental tools across biological research, enabling studies in structural biology, enzymology, interaction mapping, and more. To facilitate expression, purification, detection, and characterization of these proteins, molecular biologists routinely incorporate peptide or protein tags into expression constructs. These tags enhance solubility, streamline affinity purification workflows, and enable sensitive detection in analytical assays. This technical article provides a comprehensive overview of the most widely used recombinant protein tags, their biochemical properties, and their functional applications from a research reagent perspective.
▌Recombinant Protein Tags: Technical Overview
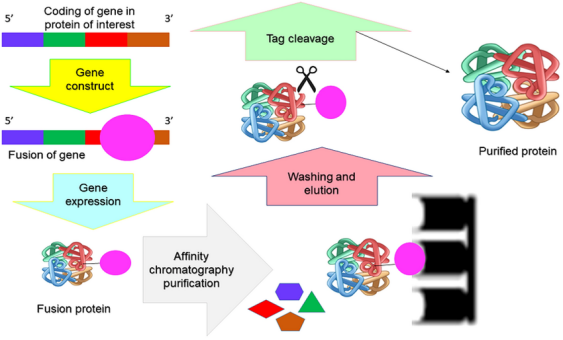
Recombinant protein tags are short peptide sequences or protein domains genetically fused to a target protein. These tags serve specific roles such as facilitating affinity purification, enhancing solubility, enabling detection with tag-specific reagents, or assisting in downstream applications like immobilization. Tags can be positioned at the N- or C terminus of the recombinant protein, depending upon the structural and functional requirements of the target protein.
1. Polyhistidine (His) Tag
The polyhistidine tag (commonly 6xHis) is one of the most pervasive affinity tags used in recombinant protein workflows. Consisting of six consecutive histidine residues, this tag binds with high affinity to immobilized metal ions such as nickel (Ni²⁺) or cobalt (Co²⁺) chelated on chromatography resins. His-tagged proteins are purified under native or denaturing conditions via immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC). Because of its small size (~0.8 kDa), the His tag minimally interferes with protein folding and function. Detection of His-tagged proteins is also facilitated through anti-His monoclonal antibodies and tag-specific probes.
2. Glutathione S-Transferase (GST) Tag
The Glutathione S-Transferase (GST) tag is a larger affinity tag (~26 kDa) derived from Schistosoma japonicum GST. The GST tag binds glutathione immobilized on solid supports, enabling single-step affinity purification of GST fusion proteins. In addition to its utility in affinity purification, the GST tag can improve the solubility of otherwise aggregation-prone recombinant proteins. Detection of GST fusion proteins in Western blotting or immunoassays is readily achieved using anti-GST antibodies.
3. Maltose-Binding Protein (MBP) Tag
Maltose-Binding Protein (MBP) is another large, highly soluble tag (~42 kDa) that enhances the solubility of fusion partners. MBP binds specifically to amylose resin through its native affinity for maltose. MBP tags facilitate purification under native conditions with high yield and purity. MBP is particularly useful when expressing challenging eukaryotic proteins or protein domains that benefit from increased folding assistance in prokaryotic expression systems.
4. FLAG Tag
The FLAG tag is a short hydrophilic peptide sequence (DYKDDDDK) that enables specific detection and affinity purification via antibody-based systems. FLAG tag reagents include anti-FLAG monoclonal antibodies, FLAG affinity resins, and detection kits compatible with Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence. Due to its small size and high specificity, the FLAG tag is often used where minimal perturbation of the target protein is critical.
5. Strep-Tag II
The Strep-Tag II is an eight-amino-acid peptide (WSHPQFEK) that interacts with engineered streptavidin or Strep-Tactin resins. This tag enables mild affinity purification with high specificity and typically elutes under gentle competitive conditions using desthiobiotin. Because of these characteristics, the Strep-Tag II system is ideal for preserving the native conformation and activity of sensitive recombinant proteins.
6. SUMO Tag
The Small Ubiquitin-like Modifier (SUMO) tag is a protein fusion partner that can enhance solubility and proper folding of recombinant proteins. SUMO tags are recognized by specific SUMO proteases that cleave precisely at the junction between the SUMO tag and the target protein, leaving no extraneous residues. SUMO fusion systems are especially valuable when expression of eukaryotic proteins in bacterial hosts results in insoluble aggregates.
7. Thioredoxin (Trx) Tag
Thioredoxin (Trx) is a small (~12 kDa) redox protein that can improve solubility and expression yields of recombinant proteins in E. coli. The Trx tag is used in affinity purification schemes coupled with tag-specific resins or in combination with polyhistidine tags for dual affinity purification strategies. Trx is particularly effective for proteins that require disulfide bond formation or increased folding assistance in reducing environments.
8. Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) and Fluorescent Protein Tags
Fluorescent protein tags such as Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) and its derivatives (e.g., mCherry, CFP, YFP) serve dual roles as affinity tags and functional reporters. These tags allow real-time visualization of recombinant protein expression, subcellular localization, and protein trafficking in live cells. GFP fusion proteins can also be purified using anti-GFP affinity reagents or tagged with additional affinity handles (e.g., His or Strep-Tag) for biochemical purification.
▌Affinity Purification and Detection Systems
Affinity purification leverages the selective interaction between a recombinant protein tag and a corresponding ligand immobilized on a solid support. Common chromatography modes used in research reagent workflows include immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC) for His tags, glutathione affinity for GST tags, amylose affinity for MBP, and streptavidin or Strep-Tactin for Strep-Tag II. Detection systems employ tag-specific antibodies or binding reagents in Western blotting, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA), and immunoprecipitation.
▌Fusion Tag Positioning
Tag placement at the N- or C terminus of the recombinant protein impacts fusion performance. N-terminal tags may enhance solubility and translation initiation, while C-terminal tags may be favorable when the N terminus is part of an active site or signal sequence. Many research reagent providers supply cloning vectors with versatile multiple cloning sites (MCS) that allow seamless insertion of coding sequences in frame with various tag options. Flexible linkers between the tag and the target protein help reduce steric interference and can improve folding and activity.
▌Tag Removal and Proteolytic Cleavage
In some research applications, the presence of a tag may interfere with functional assays or structural studies. To address this, protease recognition sites (e.g., TEV protease, thrombin, factor Xa) are introduced between the tag and the target protein. After affinity purification, site-specific proteases cleave the tag away from the protein of interest. Cleavage reactions require careful optimization to preserve protein integrity and minimize non-specific proteolysis.
▌Analytical and Downstream Applications
Tagged recombinant proteins support a wide range of analytical workflows. For example, His-tagged proteins are quantified and validated by anti-His Western blotting, while FLAG tags facilitate sensitive ELISA designs due to high specificity of anti-FLAG antibodies. Fluorescent tags such as GFP enable live-cell imaging and high-content screening. Tags also facilitate immobilization on biosensor surfaces for surface plasmon resonance (SPR) and bio-layer interferometry (BLI), enabling kinetic analyses of molecular interactions.
Recombinant protein tags remain foundational tools in modern life science research, supporting efficient purification, reliable detection, and versatile downstream applications. Familiarity with the biochemical properties and applications of common tags such as His, GST, MBP, FLAG, Strep-Tag II, SUMO, Trx, and fluorescent proteins empowers researchers to design workflows that maximize yield, purity, and analytical performance.
If you have any questions regarding recombinant protein expression systems, tag selection, or general research reagent considerations, our technical team is always available to support your work. Please feel free to contact us at info@nebulabio.cn for further technical discussion or consultation.